Treatment-resistant depression (TRD) is a form of major depressive disorder that does not respond well to standard treatments, including antidepressant medications and psychotherapy. This condition is incredibly challenging for both patients and healthcare providers, as it often leaves individuals feeling hopeless and exhausted. However, lifestyle changes can offer a powerful complement to traditional treatments and may help alleviate some of the symptoms of TRD.
While these changes are not a substitute for professional medical treatment, they can significantly enhance overall mental well-being and improve the effectiveness of other therapeutic interventions.
What is Treatment-Resistant Depression?
Before we delve into lifestyle changes, it’s important to understand what treatment-resistant depression is and how it differs from regular depression.
Treatment-resistant depression (TRD) refers to a type of depression that has not responded to at least two different antidepressant medications in conjunction with other forms of treatments (such as psychotherapy). Individuals with TRD may feel that nothing works to alleviate their symptoms, leading to frustration, worsening of depression, and a sense of helplessness.
Because traditional medications and therapies might not work for those with TRD, alternative strategies are often explored, and lifestyle changes are among the most accessible and beneficial options.
How Lifestyle Changes Can Support Treatment-Resistant Depression
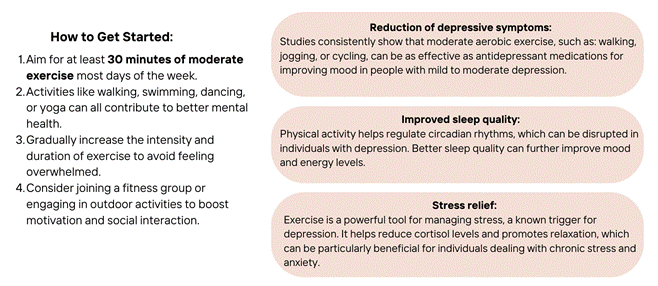
1. Exercise and Physical Activity
Regular exercise has been shown to release endorphins—often referred to as “feel-good” hormones—that can enhance mood and reduce symptoms of depression. Exercise also increases the production of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), a protein that supports brain health, promotes neuroplasticity, and has been linked to improvements in mood disorders.
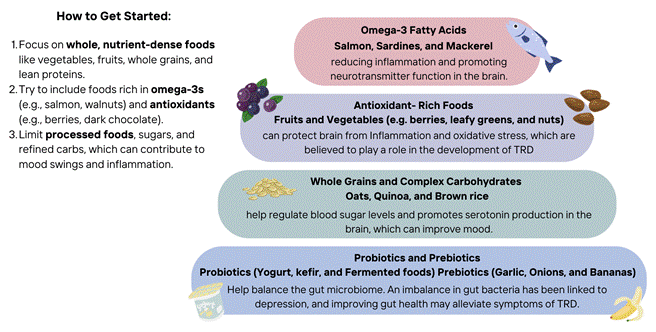
2. Nutrition and Diet
There is growing evidence to suggest that diet plays a crucial role in mental health. The gut-brain connection refers to the influence that the gut microbiome has on brain function and mood regulation. Poor diet choices—such as a high intake of processed foods, sugars, and unhealthy fats—can disrupt the balance of gut bacteria and contribute to inflammation, which is associated with depression.
On the other hand, a healthy diet rich in nutrients and anti-inflammatory foods can help improve symptoms of depression. Some dietary changes that can benefit those with treatment-resistant depression include:
3. Sleep Hygiene and Restful Sleep
Sleep disturbances are common in individuals with depression, and poor sleep can worsen symptoms of treatment-resistant depression. On the flip side, getting quality sleep can significantly improve mood, energy levels, and cognitive function.
Sleep plays a critical role in regulating mood and emotional responses. Chronic sleep deprivation can increase cortisol levels, contribute to anxiety, and disrupt emotional regulation. This can exacerbate symptoms of depression and make it more difficult for individuals to recover from a depressive episode.
How to Improve Sleep:
- Establish a sleep routine: Go to bed and wake up at the same time every day, even on weekends.
- Create a calming bedtime ritual: Engage in activities that promote relaxation, such as reading a book, practicing deep breathing, or doing gentle stretches.
- Limit screen time: Reduce exposure to screens at least one hour before bed, as the blue light emitted by phones, tablets, and computers can disrupt sleep.
- Optimize your sleep environment: Keep your bedroom dark, quiet, and cool. Consider using blackout curtains or earplugs if needed.
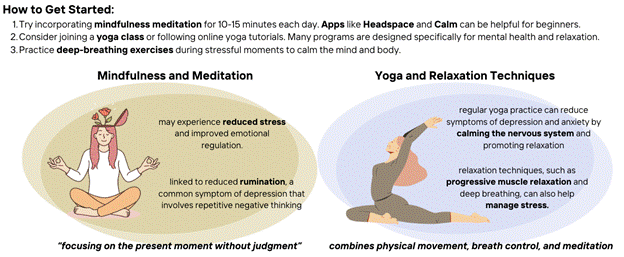
4. Stress Management and Mindfulness
Chronic stress is a major contributing factor to depression, especially in individuals with treatment-resistant depression. Mindfulness-based interventions such as meditation, yoga, and deep-breathing exercises have shown promise in reducing symptoms of depression and improving overall mental well-being.
While treatment-resistant depression can be incredibly challenging, lifestyle changes can play a critical role in alleviating symptoms and enhancing the overall treatment process. Exercise, nutrition, sleep hygiene, stress management, and social connection are all valuable tools in managing TRD. By integrating these lifestyle changes, individuals with treatment-resistant depression may find greater relief and improvement in their symptoms, paving the way for a better quality of life.
If you’re interested in learning more about Treatment-resistant depression and options for treatment, don’t hesitate to reach out to Oasis Center for Interventional Psychiatry. We can help you determine innovative treatments and work with you to create a treatment plan that addresses your unique needs along with lifestyle changes.